Topic 3.2-Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
3.2.1 Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds
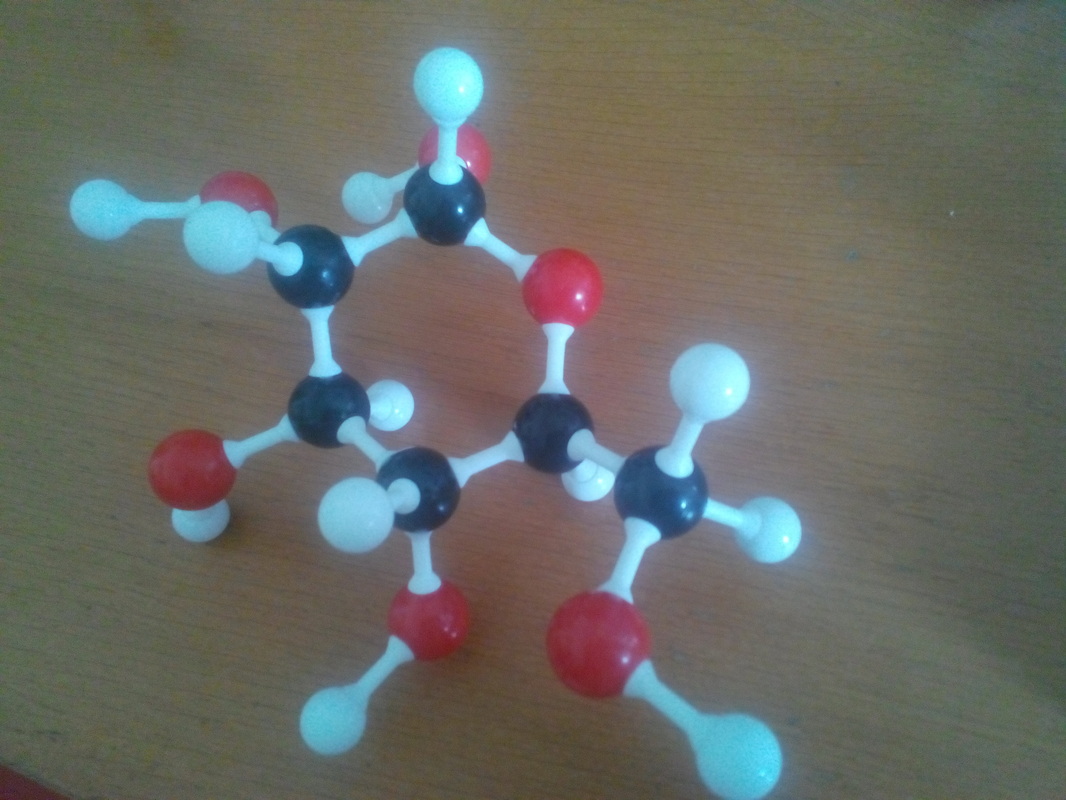
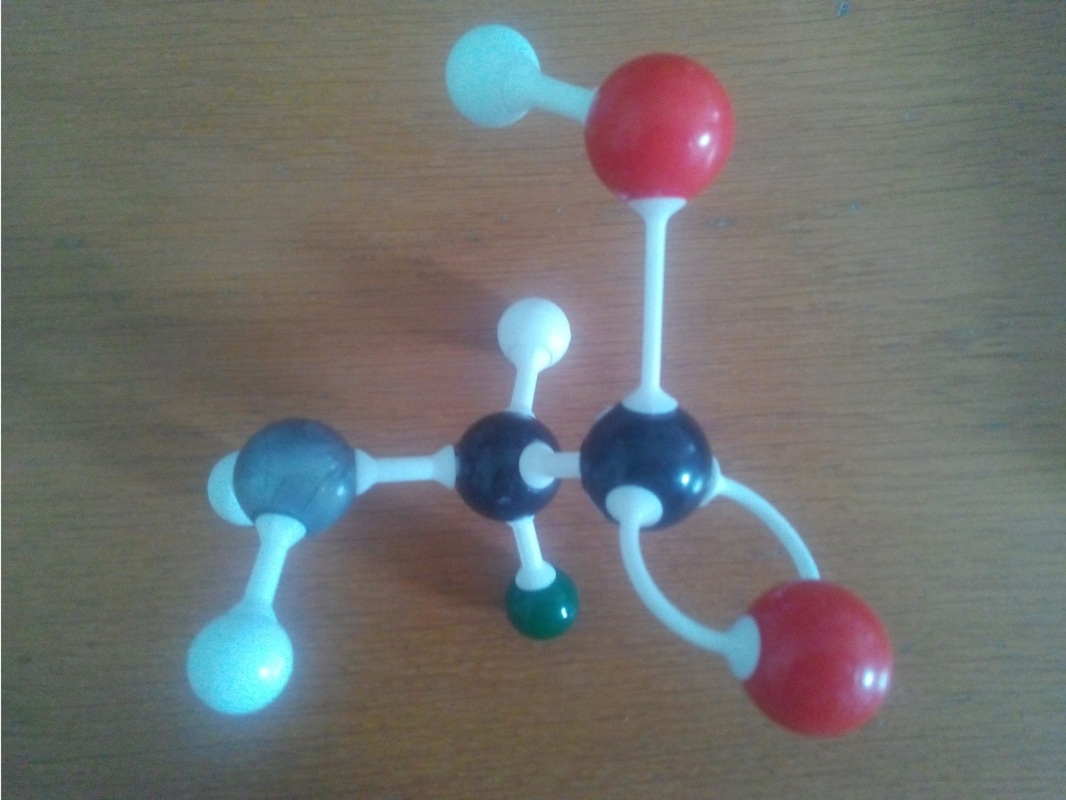
3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from diagrams showing their structure
3.2.3 List three examples each of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
3.2.4 State one function of glucose, lactose, and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose, and cellulose in plants.
3.2.5 Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides.
3.2.6 State three functions of lipids
3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage
3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from diagrams showing their structure
3.2.3 List three examples each of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
3.2.4 State one function of glucose, lactose, and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose, and cellulose in plants.
3.2.5 Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides.
3.2.6 State three functions of lipids
3.2.7 Compare the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage
Day 1
Organic and inorganic molecules
3.2.1 Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds
Watch the video. Prepare a word document and answer the following questions- (submit it in the submission form below)
1. What are inorganic molecules? give examples.
2. What is cohesion and adhesion in terms of water ?
3. Paste a picture of the drawing of a water molecule.
4. Why do aquatic organisms have a flat body?
5. What is the similarity between carbohydrate and water?
6. What are organic molecules? give examples.
7. What are the forms of carbohydrates and their uses?
8. What are lipids? Describe their structure.
9. Where are lipids present in the human body and how can they be harmful?
10. How are proteins important?
11. What are nucleic acids and what is their subunit?
1. What are inorganic molecules? give examples.
2. What is cohesion and adhesion in terms of water ?
3. Paste a picture of the drawing of a water molecule.
4. Why do aquatic organisms have a flat body?
5. What is the similarity between carbohydrate and water?
6. What are organic molecules? give examples.
7. What are the forms of carbohydrates and their uses?
8. What are lipids? Describe their structure.
9. Where are lipids present in the human body and how can they be harmful?
10. How are proteins important?
11. What are nucleic acids and what is their subunit?